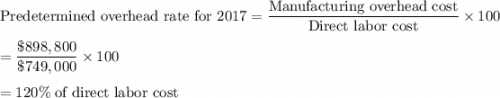Business, 22.04.2020 00:42 corbin3582
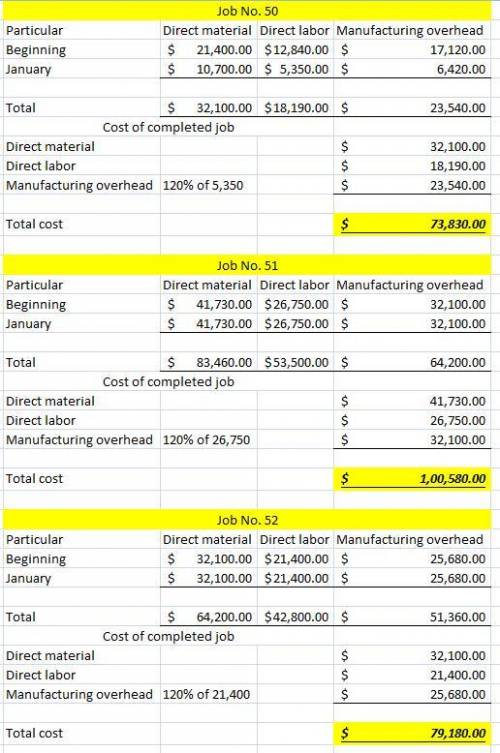
Problem 2-1A Lott Company uses a job order cost system and applies overhead to production on the basis of direct labor costs. On January 1, 2017, Job No. 50 was the only job in process. The costs incurred prior to January 1 on this job were as follows: direct materials $21,400, direct labor $12,840, and manufacturing overhead $17,120. As of January 1, Job No. 49 had been completed at a cost of $96,300 and was part of finished goods inventory. There was a $16,050 balance in the Raw Materials Inventory account. During the month of January, Lott Company began production on Jobs 51 and 52, and completed Jobs 50 and 51. Jobs 49 and 50 were also sold on account during the month for $130,540 and $169,060, respectively. The following additional events occurred during the month. 1. Purchased additional raw materials of $96,300 on account 2. Incurred factory labor costs of $74,900. Of this amount $17,120 related to employer payroll taxes. 3. Incurred manufacturing overhead costs as follows: indirect materials $18,190 indirect labor $21,400; depreciation expense on equipment $12,840 and various other manufacturing overhead costs on account $17,120 4. Assigned direct materials and direct labor to jobs as follows Job No Direct Materials Direct Labor $10,700 $5,350 50 51 41,730 26 750 52 32,100 21,400 Calculate the predetermined overhead rate for 2017, assuming Lott Company estimates total manufacturing overhead costs of $898,800, direct labor costs of $749,000, and direct labor hours of 21,400 for the year. (Round answer to the nearest whole percent, e. g. 25%.) Predetermined overhead rate Open job cost sheets for Jobs 50, 51, and 52. Enter the January 1 balances on the job cost sheet for Job No. 50 Job No. 50 Direct Materials Direct Labor Manufacturing Overhead Dat Beg Cost of completed job Direct materials Direct labor Manufacturing overhead Total cost

Answers: 2
Another question on Business

Business, 21.06.2019 15:30
Thirty years ago daniel bought a plot of land for $50,000 when the cpi was 50. now the cpi is 180 and he sold the land for $180,000. what issue might inflation cause for daniel?
Answers: 2

Business, 21.06.2019 21:00
The price of trade suppose that portugal and sweden both produce rye and wine. portugal's opportunity cost of producing a bottle of wine is 4 bushels of rye while sweden's opportunity cost of producing a bottle of wine is 10 bushels of rye. by comparing the opportunity cost of producing wine in the two countries, you can tell thatportugal/sweden has a comparative advantage in the production of wine.andportugal/sweden has a comparative advantage in the production of rye. suppose that portugal and sweden consider trading wine and rye with each other. portugal can gain from specialization and trade as long as it receives more rye for each bottle of wine it exports to sweden. similarly, sweden can gain from trade as long as it receives more bottles of wine for each bushel of rye it exports to portugal. based on your answer to the last question, which of the following prices of trade (that is, price of wine in terms of rye) would allow both sweden and portugal to gain from trade? a. 1 bushels of rye per bottle of wineb. 8 bushels of rye per bottle of winec. 9 bushels of rye per bottle of wined. 3 bushels of rye per bottle of wine
Answers: 3

Business, 21.06.2019 23:30
On september 12, ryan company sold merchandise in the amount of $5,800 to johnson company, with credit terms of 2/10, n/30. the cost of the items sold is $4,000. ryan uses the periodic inventory system and the net method of accounting for sales. on september 14, johnson returns some of the non-defective merchandise, which is restored to inventory. the selling price of the returned merchandise is $500 and the cost of the merchandise returned is $350. the entry or entries that ryan must make on september 14 is (are): multiple choice sales returns and allowances 490 accounts receivable 490 merchandise inventory 350 cost of goods sold 350 sales returns and allowances 490 accounts receivable 490 sales returns and allowances 500 accounts receivable 500 sales returns and allowances 490 accounts receivable 490 merchandise inventory 343 cost of goods sold 343 sales returns and allowances 350 accounts receivable 350
Answers: 1

Business, 22.06.2019 03:00
For each separate case below, follow the 3-step process for adjusting the prepaid asset account at december 31. step 1: determine what the current account balance equals. step 2: determine what the current account balance should equal. step 3: record the december 31 adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2. assume no other adjusting entries are made during the year. a. prepaid insurance. the prepaid insurance account has a $4,700 debit balance to start the year. a re- view of insurance policies and payments shows that $900 of unexpired insurance remains at year-end. b. prepaid insurance. the prepaid insurance account has a $5,890 debit balance at the start of the year. a review of insurance policies and payments shows $1,040 of insurance has expired by year-end. c.prepaidrent.onseptember1ofthecurrentyear,thecompanyprepaid$24,000 for 2 years of rentfor facilities being occupied that day. the company debited prepaid rent and credited cash for $24,000.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Problem 2-1A Lott Company uses a job order cost system and applies overhead to production on the bas...
Questions

History, 03.07.2019 09:20

Mathematics, 03.07.2019 09:20

Chemistry, 03.07.2019 09:20

Mathematics, 03.07.2019 09:20


History, 03.07.2019 09:20


Mathematics, 03.07.2019 09:20

Mathematics, 03.07.2019 09:20

Mathematics, 03.07.2019 09:20

Mathematics, 03.07.2019 09:20




English, 03.07.2019 09:20


Social Studies, 03.07.2019 09:20