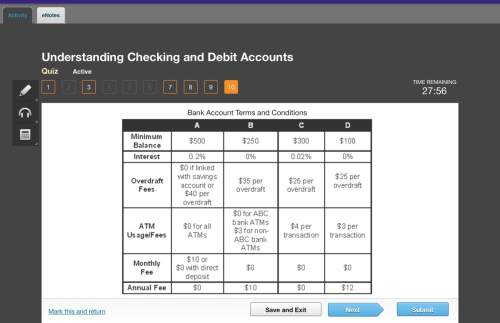
Business, 05.07.2020 16:01 raiderries
DataSpan, Inc., automated its plant at the start of the current year and installed a flexible manufacturing system. The company is also evaluating its suppliers and moving toward Lean Production. Many adjustment problems have been encountered, including problems relating to performance measurement. After much study, the company has decided to use the performance measures below, and it has gathered data relating to these measures for the first four months of operations.
Month
1234
Throughput time (days)
Delivery cycle time (days)
Manufacturing cycle efficiency (MCE)
Percentage of on-time deliveries73%74%79%86%
Total sales (units)10,550 10,440 10,56010,560
Management has asked for your help in computing throughput time, delivery cycle time, and MCE. The following average times have been logged over the last four months:
Average per Month (in days)
1234
Move time per unit0.6 0.5 0.4 0.8
Process time per unit0.7 0.7 0.7 0.4
Wait time per order before start
of production
9.6 8.0 5.0 4.0
Queue time per unit3.4 3.1 2.4 1.7
Inspection time per unit0.6 0.6 0.4 0.6
Required:
1-a. Compute the throughput time for each month. (Round your answers to 1 decimal place.)
Throughput Time
Month 1 days
Month 2 days
Month 3 days
Month 4 days
1-b.
Compute the manufacturing cycle efficiency (MCE) for each month. (Round your percentage answers to 1 decimal place (i. e., 0.1234 should be considered as 12.3%.))
Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency (MCE)
Month 1 %
Month 2 %
Month 3 %
Month 4 %
1-c.
Compute the delivery cycle time for each month. (Round your answers to 1 decimal place.)
Delivery Cycle Time
Month 1 days
Month 2 days
Month 3 days
Month 4 days
3-a.
Refer to the move time, process time, and so forth, given for month 4. Assume that in month 5 the move time, process time, and so forth, are the same as in month 4, except that through the use of Lean Production the company is able to completely eliminate the queue time during production. Compute the new throughput time and MCE. (Round your answers to 1 decimal place.)
Month 5
Throughput time days
Manufacturing cycle efficiency (MCE) %
3-b.
Refer to the move time, process time, and so forth, given for month 4. Assume in month 6 that the move time, process time, and so forth, are again the same as in month 4, except that the company is able to completely eliminate both the queue time during production and the inspection time. Compute the new throughput time and MCE. (Round your answers to 1 decimal place.)
Month 6
Throughput time days
Manufacturing cycle efficiency (MCE) %

Answers: 3
Another question on Business

Business, 22.06.2019 11:20
Which stage of group development involves members introducing themselves to each other?
Answers: 3

Business, 22.06.2019 11:50
Select the correct answer. ramon applied to the state university in the city where he lives, but he was denied admission. what should he do now? a.change his mind about graduating and drop out of high school so he can start working right away. b. decide not to go to college, because he didn’t have a backup plan. c.stay positive and write a mean letter to let the college know that they made a bad decision. d. learn from this opportunity, reevaluate his options, and apply to his second and third choices.
Answers: 2

Business, 22.06.2019 14:20
In canada, the reference base period for the cpi is 2002. by 2012, prices had risen by 21.6 percent since the base period. the inflation rate in canada in 2013 was 1.1 percent. calculate the cpi in canada in 2013. hint: use the information that “prices had risen by 21.6 percent since the base period” to find the cpi in 2012. use the inflation rate formula (inflation is the growth rate of the cpi) to find cpi in 2013, knowing the cpi in 2012 and the inflation rate. the cpi in canada in 2013 is round up your answer to the first decimal. 122.9 130.7 119.6 110.5
Answers: 1

Business, 22.06.2019 20:40
Answer the questions about keynesian theory, market economics, and government policy. keynes believed that there were "sticky" wages and that recessions are caused by increases in prices. decreases in supply. decreases in aggregate demand (ad). increases in unemployment. keynes believed the government should increase ad through increased government spending, but not tax cuts. control wages to increase employment because of sticky wages. increase employment through tax cuts only. increase as through tax cuts. increase ad through either increased government spending or tax cuts. intervene when individual markets fail by controlling prices and production.
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
DataSpan, Inc., automated its plant at the start of the current year and installed a flexible manufa...
Questions


Biology, 19.03.2021 21:40





Mathematics, 19.03.2021 21:40

History, 19.03.2021 21:40







Social Studies, 19.03.2021 21:40

Health, 19.03.2021 21:40


Mathematics, 19.03.2021 21:40