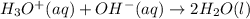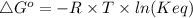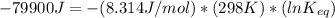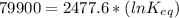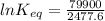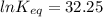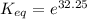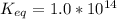Chemistry, 14.07.2019 10:30 samantha636
The standard free energy change for the formation of two moles of h2o(l) in a strong acid–strong base neutralization reaction at 25°c is -79.9kj. calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction. see equation 11.1. h3o+(aq) + oh-(aq) = 2 h2o (l)

Answers: 1
Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 00:00
Substance x has a fixed volume, and the attraction between its particles is strong .substance y had widely spread out particles and can be compressed what can most likely be concluded about these substances
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 10:30
Astudent reacts 13 moles of iron with 21 moles of oxygen according to the following equation:
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 11:40
Effect of rotenone and antimycin a on electron transfer rotenone, a toxic natural product from plants, strongly inhibits nadh dehydrogenase of insect and fish mitochondria. antimycin a, a toxic antibiotic, strongly inhibits the oxidation of ubiquinol. (a) explain why rotenone ingestion is lethal to some insect and fish species. (b) explain why antimycin a is a poison. (c) given that rotenone and antimycin a are equally effective in blocking their respective sites in the electron-transfer chain, which would be a more potent poison? explain.
Answers: 3

You know the right answer?
The standard free energy change for the formation of two moles of h2o(l) in a strong acid–strong bas...
Questions




Mathematics, 12.12.2019 13:31

History, 12.12.2019 13:31

Business, 12.12.2019 13:31

Mathematics, 12.12.2019 13:31

Social Studies, 12.12.2019 13:31








Mathematics, 12.12.2019 13:31


Geography, 12.12.2019 13:31


Mathematics, 12.12.2019 13:31