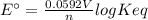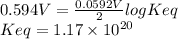Chemistry, 30.11.2019 02:31 mhuerta71001
Interactive activity—the relationship among e°cell, keq, and gibbs free energy in an electrochemical cell, the potential difference between two electrodes under standard conditions is known as the standard cell potential (e∘cell). the standard cell potential can be used to identify the overall tendency of a redox reaction to occur spontaneously. the spontaneity of a reaction is identified using the gibbs free energy δg∘. δg∘ is related to e∘cell. e∘cell and δg∘ are also related to equilibrium constant keq of the reaction. select the image to explore the activity that shows how e∘cell, keq, and δg∘ are related to each other. launch activity in the activity, you should see a triangle, whose three vertices represent keq, e∘cell, and δg∘. you can select two vertices and determine the relation between them. you can then reset the activity and select the next two quantities. constants the following values may be useful when solving this tutorial. constant value e∘cu 0.337 v e∘ni -0.257 v r 8.314 j⋅mol−1⋅k−1 f 96,485 c/mol t 298 k part a in the activity, click on the e∘cell and keq quantities to observe how they are related. use this relation to calculate keq for the following redox reaction that occurs in an electrochemical cell having two electrodes: a cathode and an anode. the two half-reactions that occur in the cell are cu2+(aq)+2e−→cu(s) and ni(s)→ni2+(aq)+2e− the net reaction is cu2+(aq)+ni(s)→cu(s)+ni2+(aq) use the given standard reduction potentials in your calculation as appropriate. express your answer numerically to three significant figures.

Answers: 2
Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 04:30
Use the drop-down menus to answer each question. which runner finished the 100 m race in the least amount of time? which runner stopped running for a few seconds during the race? at what distance did anastasia overtake chloe in the race?
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 11:40
Effect of rotenone and antimycin a on electron transfer rotenone, a toxic natural product from plants, strongly inhibits nadh dehydrogenase of insect and fish mitochondria. antimycin a, a toxic antibiotic, strongly inhibits the oxidation of ubiquinol. (a) explain why rotenone ingestion is lethal to some insect and fish species. (b) explain why antimycin a is a poison. (c) given that rotenone and antimycin a are equally effective in blocking their respective sites in the electron-transfer chain, which would be a more potent poison? explain.
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 18:20
Which reason best explains why metals are malleable? a)because they have delocalized electrons b)because they have localized electrons c)because they have ionic bonds d)because they have rigid bonds
Answers: 2

You know the right answer?
Interactive activity—the relationship among e°cell, keq, and gibbs free energy in an electrochemical...
Questions

Mathematics, 14.07.2020 15:01





Mathematics, 14.07.2020 15:01

Mathematics, 14.07.2020 15:01





Mathematics, 14.07.2020 15:01






Mathematics, 14.07.2020 15:01