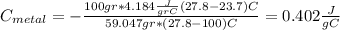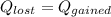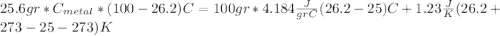For the following scenarios what is the metal? a piece of metal weighing 59.047 g was heated to 100.0 degree c and then put it into 100.0 ml of water (initially at 23.7 degree c). the metal and water were allowed to come to an equilibrium temperature, determined to be 27.8 degree c. assuming no heat lost to the environment, calculate the specific heat of the metal. a 25.6 g piece of metal was taken from a beaker of boiling water at 100.0 degree c and placed directly into a calorimeter holding 100.0 ml of water at 25.0 degree c. the calorimeter heat capacity is 1.23 j/k. given that the final temperature at thermal equilibrium is 26.2 degree c, determine the specific heat capacity of the metal.

Answers: 1
Another question on Chemistry


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 15:30
Plz me ! 1 which of earths spheres contains most of its mass? a atmosphere b hydrosphere c geosphere* d biosphere 2 erosion and weathering are examples of which types of forces? a constructive forces b destructive forces* c gravitational forces d inertia-related forces 3 which of the following statements about earths atmosphere is true? a earths atmosphere contains 78% water vapor which is essentail to life b earths atmosphere contains 21% oxygen c earths atmosphere contains carbon dioxide which all life forms require d earths atmosphere allows radiation from the sun to pass through it and warm earths surface* 4 the strenght of the force of gravity between two objects is determined by which of the following factors? select all that apply a the messes of the objects* b the distance between the objects* c the volumes of the objects d the surface area of the objects 5 earth and moon are kept in there respective orbits due to the influence of a inertia b gravity c gravity and inertia* d neither gravity or inertia if you answer all questions right i will give
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 20:00
Many free radicals combine to form molecules that do not contain any unpaired electrons. the driving force for the radical–radical combination reaction is the formation of a new electron‑pair bond. consider the chemical equation. n(g)+no(g)⟶nno(g) n(g)+no(g)⟶nno(g) write lewis formulas for the reactant and product species in the chemical equation. include nonbonding electrons. n(g)n(g) select draw rings more erase select draw rings more erase select draw rings more erase n no(g)
Answers: 1

You know the right answer?
For the following scenarios what is the metal? a piece of metal weighing 59.047 g was heated to 100...
Questions

Physics, 27.08.2019 02:50


History, 27.08.2019 02:50

Physics, 27.08.2019 02:50


Biology, 27.08.2019 02:50

Mathematics, 27.08.2019 02:50


History, 27.08.2019 02:50

English, 27.08.2019 02:50




English, 27.08.2019 02:50



History, 27.08.2019 02:50

World Languages, 27.08.2019 02:50

Mathematics, 27.08.2019 02:50

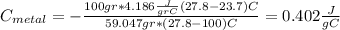
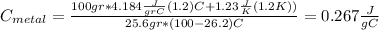
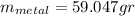 the mass of the metal
the mass of the metal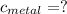 Is the value that we need to find
Is the value that we need to find represent the final temperature of equilibrium for the metal and the water
represent the final temperature of equilibrium for the metal and the water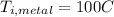 represent the initial temperature for the metal
represent the initial temperature for the metal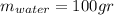 since the density is 1g/ml
since the density is 1g/ml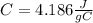 the specific heat for the liquid water
the specific heat for the liquid water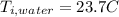 the initial temperature for the water
the initial temperature for the water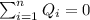 if we have balance then we have this:
if we have balance then we have this: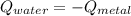
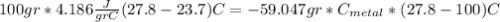
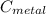 we got:
we got: