Chemistry, 15.02.2020 01:18 quintinjerome
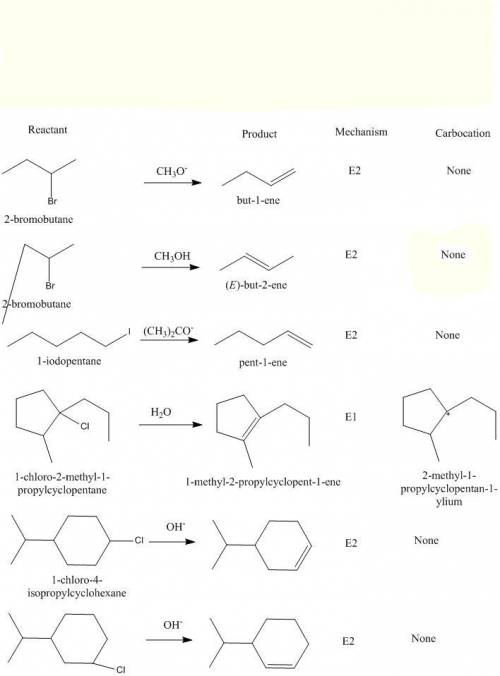
Dehydrohalogenation is the loss of hydrogen and a halogen from an alkyl halide. It is one of the most useful methods for preparing alkenes by elimination. The synthesis can occur by two mechanisms, E1 and E2. The E1 mechanism is a two-step reaction: in the first step, the bond to the leaving group breaks forming an intermediate carbocation and in the second step, a base removes a proton from the ?-carbon (carbon that is adjacent to the carbon bearing the leaving group), giving place to the formation of a double bond. The E2mechanism takes place in only one step: the bond to the leaving group breaks at the same time as the double bond is formed. In this mechanism, no intermediate is formed. Which reaction occurs is determined by the reaction conditions employed.
Predict the mechanism that the following reactions will undergo for the given conditions. If applicable, indicate the correct structure of the carbocation intermediate. For the reactions that do not have a carbocation intermediate, add the label "none" to the carbocation column.
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.

Answers: 1
Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 14:30
Find the protons, electrons and neutrons for strontium with a mass of 83
Answers: 1


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 16:00
No copying 15 pts how does a free-body diagram tell you about the net force on an object?
Answers: 2

You know the right answer?
Dehydrohalogenation is the loss of hydrogen and a halogen from an alkyl halide. It is one of the mos...
Questions

Biology, 05.05.2020 18:30

Mathematics, 05.05.2020 18:30


Mathematics, 05.05.2020 18:30


Mathematics, 05.05.2020 18:31

Mathematics, 05.05.2020 18:31









Mathematics, 05.05.2020 18:31



Mathematics, 05.05.2020 18:31