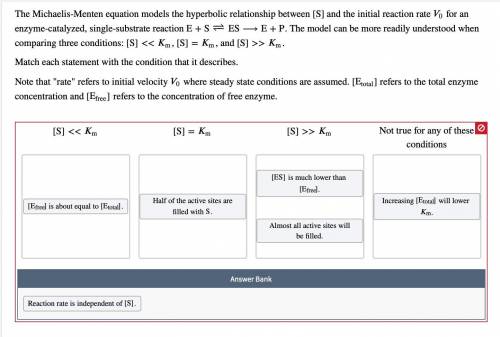
Enzyme‑catalyzed, single‑substrate reaction E + S − ⇀ ↽ − ES ⟶ E + P . The model can be more readily understood when comparing three conditions: [ S ] << K m , [ S ] = K m , and [ S ] >> K m . Match each statement with the condition that it describes. Note that "rate" refers to initial velocity V 0 where steady state conditions are assumed. [ E total ] refers to the total enzyme concentration and [ E free ] refers to the concentration of free enzyme.

Answers: 1
Another question on Chemistry


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 22:40
Percent ionization for a weak acid (ha) is determined by the following formula: percent ionization=[ha] ionized[ha] initial×100%for strong acids, ionization is nearly complete (100%) at most concentrations. however, for weak acids, the percent ionization changes significantly with concentration. the more diluted the acid is, the greater percent ionization.a certain weak acid, ha, has a ka value of 9.4×10? 7.part acalculate the percent ionization of ha in a 0.10 m solution.part bcalculate the percent ionization of ha in a 0.010 m solution
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 23:00
What is formed when amino acids form long chains or polymerize
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 23.06.2019 21:30
Hno3 + s → h2so4 + no break down the equation shown into the skeletal half-reactions for oxidation and reduction. which of these pairs shows the two skeletal half-reactions with their correct assignments?
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Enzyme‑catalyzed, single‑substrate reaction E + S − ⇀ ↽ − ES ⟶ E + P . The model can be more readily...
Questions


Mathematics, 17.04.2020 23:45








Mathematics, 17.04.2020 23:45

Mathematics, 17.04.2020 23:45

Advanced Placement (AP), 17.04.2020 23:46


English, 17.04.2020 23:46






![[E_{free}]](/tpl/images/0559/9062/6dbaa.png) is about | sites are filled of | independent of |
is about | sites are filled of | independent of | ![[E_{Total}]](/tpl/images/0559/9062/1b008.png) will
will ![[E_{total}]](/tpl/images/0559/9062/eeaac.png) . | | [S] | lower KM
. | | [S] | lower KM![[ES]](/tpl/images/0559/9062/41e39.png) is mathematically represented as
is mathematically represented as ![[ES] = \frac{[E_{total}][S]}{K_M + [S]}----(1)](/tpl/images/0559/9062/7c1ac.png)
![[S]](/tpl/images/0559/9062/7efa5.png) is the substrate concentration and
is the substrate concentration and 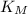 is the Michaelis constant
is the Michaelis constant ![[S] < < K_M](/tpl/images/0559/9062/087d2.png)
![[ES] = \frac{[E_{total}][S]}{K_M}](/tpl/images/0559/9062/c5287.png)
![\frac{[S]}{K_M} < < 1](/tpl/images/0559/9062/f55f6.png)
![[ES] < < [E_{total}]](/tpl/images/0559/9062/9f387.png)
![E_{free}]](/tpl/images/0559/9062/d6fa2.png) i.e the concentration of free enzymes is almost equal to
i.e the concentration of free enzymes is almost equal to ![[S] = K_M](/tpl/images/0559/9062/b6ac7.png)
![[ES] = \frac{[E_{total}][S]}{2[S]} = \frac{[E_{total}]}{2}](/tpl/images/0559/9062/e7767.png)
![[S] K_M](/tpl/images/0559/9062/f4f62.png)
![[ES] = \frac{[E_{total}] [S]}{[S]} = [E_{total}]](/tpl/images/0559/9062/51842.png)
![v =\frac{V_{max}[S]}{K_M [S]}](/tpl/images/0559/9062/bd0db.png)
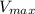 is he maximum velocity of the reaction
is he maximum velocity of the reaction![v = \frac{V_{max}[S]}{[S]} = V_{max}](/tpl/images/0559/9062/d94fd.png)