Chemistry, 04.04.2020 10:53 Cooldude3966
A simple equation relates the standard free‑energy change, ΔG∘′, to the change in reduction potential. ΔE0′. ΔG∘′ = −nFΔE0′ The n represents the number of transferred electrons, and F is the Faraday constant with a value of 96.48 kJ⋅mol^(−1)⋅V^(−1). Use the standard reduction potentials provided to determine the standard free energy released by reducing O2 with FADH2. FADH2 + 1/2O2 → FAD + H2O
given that the standard reduction potential for the reduction of oxygen to water is +0.82 V and for the reduction of FAD to FADH2 is +0.03 V.

Answers: 1
Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 02:00
Which of the following happens during cell division? (a) energy is created (b) waste is eliminated (c) carbon dioxide is released (d) damaged cells are replaced
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 07:30
Which of the following best supports the concept that genetic information is passed on to offspring from both of their parents, not just one?
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 11:50
Which of the following statements about hybrid orbitals is or are true? choose all that apply. choose all that apply. under sp2 hybridization, the large lobes point to the vertices of an equilateral triangle. after an atom undergoes sp hybridization there is one unhybridized p orbital on the atom. the angle between the large lobes of sp3 hybrids is 109.5∘
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 20:30
We are hoping to create 5.72 grams of glucose. the plant was given 4.75 liters of co2 and 2.81 g of h20. which reactant was the limiting reagent? how much excess mass did we have of the other reactant?
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
A simple equation relates the standard free‑energy change, ΔG∘′, to the change in reduction potentia...
Questions



Geography, 30.01.2021 05:30


Mathematics, 30.01.2021 05:30

Biology, 30.01.2021 05:30




English, 30.01.2021 05:30

History, 30.01.2021 05:30

Mathematics, 30.01.2021 05:30

Health, 30.01.2021 05:30


Mathematics, 30.01.2021 05:40

Biology, 30.01.2021 05:40

Mathematics, 30.01.2021 05:40


Mathematics, 30.01.2021 05:40

Mathematics, 30.01.2021 05:40

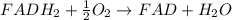
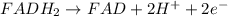
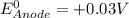
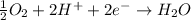
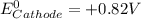
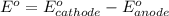
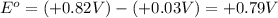
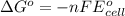
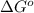 = standard free energy = ?
= standard free energy = ?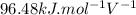
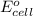 = standard electrode potential of the cell = 0.79 V
= standard electrode potential of the cell = 0.79 V