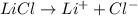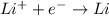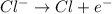Chemistry, 27.12.2020 14:00 saraaaalynn19061
Please help!-- 20 pts!
The electrolyte lithium chloride (LiCl) dissolves into positively charged Li+ and negatively charged Cl– ions in water containing electrodes.
What will happen next?
The positively charged ions will be attracted to the negative electrode and gain electrons. Meanwhile, the negatively charged ions will be attracted to the positive electrode and release electrons.
The negatively charged ions will be attracted to the negative electrode and release electrons. Meanwhile, the positively charged ions will be attracted to the positive electrode and gain electrons.
The positively charged ions will be attracted to the negative electrode and release electrons. Meanwhile, the negatively charged ions will be attracted to the positive electrode and gain electrons.
The negatively charged ions will be attracted to the negative electrode and gain electrons. Meanwhile, the positively charged ions will be attracted to the positive electrode and release electrons.

Answers: 2
Another question on Chemistry


Chemistry, 21.06.2019 23:00
Esign techniques and materials that reduce the negative environmental impact of a structure are referred to as
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 06:00
Oxidation-reduction reactions (often called "redox" for short) are reactions that involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another. oxidation states, or oxidation numbers, allow chemists to keep track of these electron transfers. in general, one element will lose electrons (oxidation), with the result that it will increase in oxidation number, and another element will gain electrons (reduction), thereby decreasing in oxidation number. the species that is oxidized is called the reducing agent or reductant. the species that is reduced is called the oxidizing agent or oxidant. to sum up: oxidation = increase in oxidation state = loss of electrons = reducing agent reduction = decrease in oxidation state = gain of electrons = oxidizing agent part a which element is oxidized in this reaction? fe2o3+3co→2fe+3co2 enter the elemental symbol. view available hint(s) is oxidized part b which element is reduced in this reaction? 2hcl+2kmno4+3h2c2o4→6co2+2mno2+2kcl+4h2o enter the elemental symbol. view available hint(s) is reduced
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 22:30
Molecular iodine, i2(g), dissociates into iodine atoms at 625 k with a first-order rate constant of 0.271 s−1. part a part complete what is the half-life for this reaction?
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Please help!-- 20 pts!
The electrolyte lithium chloride (LiCl) dissolves into positively charged Li...
Questions



Mathematics, 04.12.2021 05:10


Mathematics, 04.12.2021 05:10



History, 04.12.2021 05:10

Computers and Technology, 04.12.2021 05:20




Mathematics, 04.12.2021 05:20

Engineering, 04.12.2021 05:20



Health, 04.12.2021 05:20

Health, 04.12.2021 05:20

English, 04.12.2021 05:20