
Computers and Technology, 15.09.2021 16:30 Abarrett7323
Add the following lines to StringExplorer to see for yourself that indexOf behaves as specified:int notFoundPsn = sample. indexOf("slow");
System. out. println("sample. indexOf(\"slow\") = " + notFoundPsn);
Read the description of indexOf(String str, int fromIndex). Notice that there are two indexOf methods, however, they have different parameters. What are the differences between indexOf(String str)text annotation indicator and indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)text annotation indicator? The substring method also occurs twice. Read the description so you understand the difference between the two.
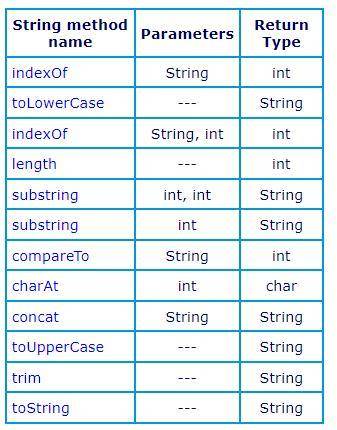
Review the methods in the following table. Notice the parameters and return type of each method. Look at the method descriptions in the String API. Once you understand what each method does, add lines to StringExplorer that illustrate each of the methods in the table. Include comment lines that state each method you are demonstrating as shown in the two examples.

Answers: 1
Another question on Computers and Technology

Computers and Technology, 22.06.2019 10:00
When is an original work considered public domain? a. when posted via social media b. when it is posted on the internet c. when a copyright symbol is not included with the piece of work d. when explicit permission is given by the author / owner
Answers: 1

Computers and Technology, 22.06.2019 11:10
Look at the far left lane in the picture. explain what the red car is doing and what it needs to do to travel safely.
Answers: 2

Computers and Technology, 22.06.2019 19:20
Terri needs to insert a cover page into her document. where should she go to access the commands to do so? o insert tab, objects group o insert tab, illustrations group o insert tab, pages group o insert tab, media group submit
Answers: 1

Computers and Technology, 23.06.2019 17:30
When making changes to optimize part of a processor, it is often the case that speeding up one type of instruction comes at the cost of slowing down something else. for example, if we put in a complicated fast floating-point unit, that takes space, and something might have to be moved farther away from the middle to accommodate it, adding an extra cycle in delay to reach that unit. the basic amdahl's law equation does not take into account this trade-off. a. if the new fast floating-point unit speeds up floating-point operations by, on average, 2ă—, and floating-point operations take 20% of the original program's execution time, what is the overall speedup (ignoring the penalty to any other instructions)? b. now assume that speeding up the floating-point unit slowed down data cache accesses, resulting in a 1.5ă— slowdown (or 2/3 speedup). data cache accesses consume 10% of the execution time. what is the overall speedup now? c. after implementing the new floating-point operations, what percentage of execution time is spent on floating-point operations? what percentage is spent on data cache accesses?
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Add the following lines to StringExplorer to see for yourself that indexOf behaves as specified:int...
Questions


Physics, 20.09.2019 09:30




Mathematics, 20.09.2019 09:30

Mathematics, 20.09.2019 09:30

Mathematics, 20.09.2019 09:30


History, 20.09.2019 09:30

Social Studies, 20.09.2019 09:30




Biology, 20.09.2019 09:30

Health, 20.09.2019 09:30

Mathematics, 20.09.2019 09:30

Mathematics, 20.09.2019 09:30


History, 20.09.2019 09:30



