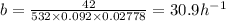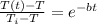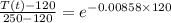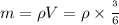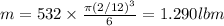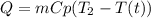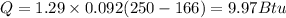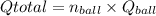Engineering, 31.10.2019 06:31 reetajmahfouz3816
In a manufacturing facility, 2-in-diameter brass balls (k = 64.1 btu/h· ft·°f, rho = 532 lbm/ft3 , and cp = 0.092 btu/lbm·°f) initially at 250°f are quenched in a water bath at 120°f for a period of 2 min at a rate of 120 balls per minute . if the convection heat transfer coefficient is 42 btu/h·ft2 ·f, determine
(a) the temperature of the balls after quenching and (b) the rate at which heat needs to be removed from the water in order to keep its temperature constant at 120°f.

Answers: 1
Another question on Engineering

Engineering, 03.07.2019 15:10
If you were designing a bumper for a car, would you prefer it to exhibit elastic or plastic deformation? why? consider the functions of a bumper in both a minor "fender-bender" and a major collision.
Answers: 1

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10
Abrake has a normal braking torque of 2.8 kip in and heat-dissipating cast-iron surfaces whose mass is 40 lbm. suppose a load is brought to rest in 8.0 s from an initial angular speed of 1600 rev/min using the normal braking torque; estimate the temperature rise of the heat dissipating surfaces.
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10
Fluids at rest possess no flow energy. a)- true b)- false
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10
The higher the astm grain-size number, the coarser the grain is. a)-true b)-false
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
In a manufacturing facility, 2-in-diameter brass balls (k = 64.1 btu/h· ft·°f, rho = 532 lbm/ft3 , a...
Questions


Mathematics, 08.09.2021 23:50




Biology, 08.09.2021 23:50




Chemistry, 08.09.2021 23:50


Mathematics, 08.09.2021 23:50






Mathematics, 08.09.2021 23:50

History, 08.09.2021 23:50

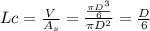
![Lc = \frac{\frac{2}{12} ft}{6} = 0.02778 ft[tex]Bi = \frac{hL}{k} = \frac{42 \times 0.02778}{64.1} = 0.01820](/tpl/images/0353/9270/98fa7.png)