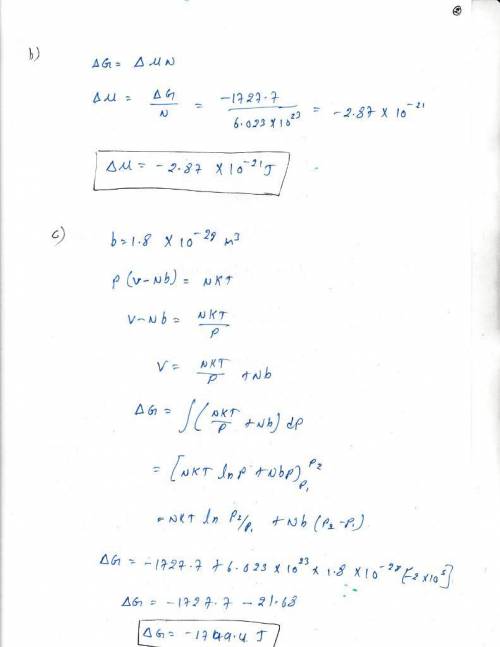Engineering, 19.12.2019 05:31 mxltie1651
1moles of a gas are initially initially under pressure 4 × 105 pa at t=300 k. in this problem, you will want to use the following relationships: definition of gibbs free energy: g=u−ts+pv equipartition: u=ndof2nkt+constentropy of an ideal gas: s=nklnv+const ideal gas law: pv=nktequation of state for system with excluded volume b: (v−nb)p=nkt
1)if the gas is ideal, how much does g change when the gas is allowed to expand isothermally until the pressure is reduced to 2 × 105 pa?
answer = -1729
2)how much did the chemical potential, change in part (1)? ? final-? initial= ?
3) now assume the gas has no interaction energy but does have an excluded volume per particle, b=1.9 × 10-28 m3, which means that s = nk ln(v-nb) + f(t, n) , where f is some function you won't need to know since t and n don't change. how much does g change when the gas expands isothermally until the pressure is reduced from 4 × 105 pa to 2 × 105pa? gfinal-ginitial= ?
4) how much did the chemical potential change in the process of part (3)? ? final-? initial= ?

Answers: 3
Another question on Engineering

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:20
Agas mixture consists of 8 kmol of h2 and 2 kmol of n2. determine the mass of each gas and the apparent gas constant of the mixture.
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:20
Air is compressed isentropically from an initial state of 300 k and 101 kpa to a final temperature of 1000 k. determine the final pressure using the following approaches: (a) approximate analysis (using properties at the average temperature) (b) exact analysis
Answers: 1

Engineering, 04.07.2019 19:20
At steady state, air at 200 kpa, 325 k, and mass flow rate of 0.5 kg/s enters an insulated duct having differing inlet and exit cross-sectional areas. the inlet cross-sectional area is 6 cm2. at the duct exit, the pressure of the air is 100 kpa and the velocity is 250 m/s. neglecting potential energy effects and modeling air as an 1.008 kj/kg k, determine ideal gas with constant cp = (a) the velocity of the air at the inlet, in m/s. (b) the temperature of the air at the exit, in k. (c) the exit cross-sectional area, in cm2
Answers: 2

Engineering, 04.07.2019 19:20
Aseries piping system conveys methyl alcohol. the system consists of 70 m of 1- nominal pipe follow by 50 m of 2-nominal pipe, both schedule 40 commercial steel. the 1-nominal pipe contains 3 90° elbows (regular) anda fully open gate valve, all threaded. the pressure drop through the system is 150 kpa. determine the volume flow rate through the system that is horizontally laid.
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
1moles of a gas are initially initially under pressure 4 × 105 pa at t=300 k. in this problem, you w...
Questions

Mathematics, 20.04.2020 17:07

Social Studies, 20.04.2020 17:07


History, 20.04.2020 17:08






History, 20.04.2020 17:08




Biology, 20.04.2020 17:09

Business, 20.04.2020 17:09


Mathematics, 20.04.2020 17:09


Mathematics, 20.04.2020 17:09