
Mathematics, 22.01.2020 00:31 cathydaves
Show that if x ∼ geom(p) then p(x = n + k|x > n) = p(x = k), for every n, k ≥ 1. this one of the ways to define the memoryless property of the geometric distribution. it states the following: given that there are no successes in the first n trials, the probability that the first success comes at trial n + k is the same as the probability that a freshly started sequence of trials yields the first success at trial k.

Answers: 1
Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 14:00
Me. drysdale earned 906.25 in interest in one year on money that he had deposited in his local bank if the bank paid an interest rate of 6.25% how much money did mr. drysdale deposit
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:00
Find all solutions for 2y - 4x =2 y = 2x + 1 site: socratic.org
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 00:30
Anew test for ra is being developed. the test is administered to 750 patients with ra and 750 without ra. for the sake of the question, assume the prevalence of ra in this population is 50%. of the 750 patients with ra, 575 have a positive result. of the 750 patients without ra, 150 have a positive result. what is the positive predictive value of the new test? a575/(575+150) b. 600/(600+ 150) c. 575/(575+125) d. 600/(600+ 125)
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 03:30
Jack brought 12 pet monkeys. if each monkey cost $45.99, how much money did he spend in all?
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Show that if x ∼ geom(p) then p(x = n + k|x > n) = p(x = k), for every n, k ≥ 1. this one of the...
Questions

Computers and Technology, 11.03.2020 03:34

Mathematics, 11.03.2020 03:34




History, 11.03.2020 03:34





Biology, 11.03.2020 03:34


Biology, 11.03.2020 03:34

Computers and Technology, 11.03.2020 03:34






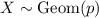 ,
, 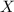 has PMF
has PMF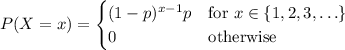
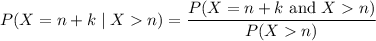
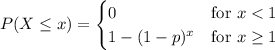
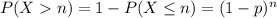
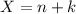 and
and 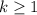 , then it's always true that
, then it's always true that 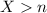 , so
, so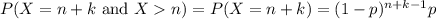
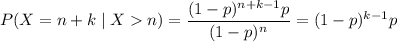
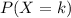 according to the PMF.
according to the PMF.

