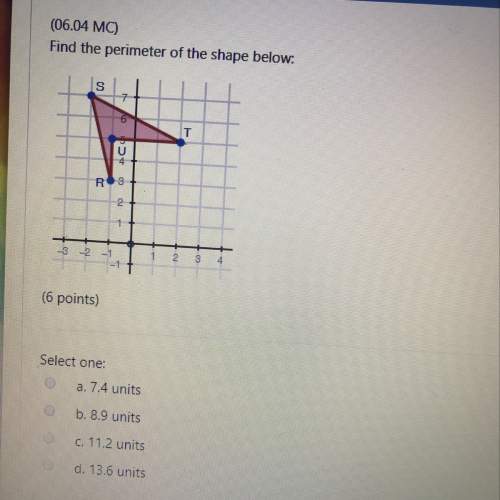
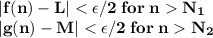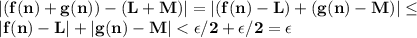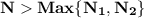Mathematics, 10.11.2019 02:31 pakabigail4796
Given a sequence f: z+→r of real numbers, we say that the sequence converges to a real number l if for all ε> 0, there exists a positive integer n such that for any positive integer n, if n≥n, then |f(n)-l|< ε. prove that if a sequence f converges to l and a sequence g converges to m, then the sequence f+g converges to l+m. (you may use the triangle inequality: |a+b|≤|a|+|b| for any real numbers a and b.)

Answers: 2
Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:20
Match each statement with its corresponding value for the system below: y = -2(3)x and y = 9x - 2 1. the number of points of intersection. -2 2. the x-coordinate of the solution. 1 3. the y-coordinate of the solution. 0
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:50
The graph represents the gallons of water in a water tank with respect to the number of hours since it was completely filled
Answers: 1


You know the right answer?
Given a sequence f: z+→r of real numbers, we say that the sequence converges to a real number l if f...
Questions

Mathematics, 05.02.2020 04:43

Biology, 05.02.2020 04:43






Mathematics, 05.02.2020 04:44





History, 05.02.2020 04:44





Mathematics, 05.02.2020 04:44


History, 05.02.2020 04:44

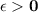 there exists
there exists  and
and 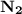 such that
such that