
Mathematics, 03.03.2020 03:33 sophialoperx
Linear differential equations sometimes occur in which one or both of the functions p(t) and g(t) for y′+p(t)y=g(t) have jump discontinuities. If t0 is such a point of discontinuity, then it is necessary to solve the equation separately for t < t0 and t > t0. Afterward, the two solutions are matched so that y is continuous at t0; this is accomplished by a proper choice of the arbitrary constants. The following problem illustrates this situation. Note that it is impossible also to make y′ continuous at t0.
Solve the initial value problem.
y' + 6y = g(t), y(0) = 0
where
g(t) = 1, 0 ≤ t ≤ 1,
= 0, t > 0.

Answers: 2
Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:30
Which elements in the set below are integers? 12, –3⁄4,√ 25 , –7, √ 5 , 14⁄7, 9 a. 12, √ 25 , –7, 9 b. 12, √ 25 , –7, 14⁄7, 9 c. –3⁄4, 25 , √ 5 ,14⁄7 d. 12, –7, 9
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:50
Which translation maps the vertex of the graph of the function f(x) = x2 onto the vertex of the function g(x) = x2 – 10x +2?
Answers: 1


Mathematics, 22.06.2019 00:00
The construction of copying qpr is started below. the next step is to set the width of the compass to the length of ab. how does this step ensure that a new angle will be congruent to the original angle?
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Linear differential equations sometimes occur in which one or both of the functions p(t) and g(t) fo...
Questions

Mathematics, 09.03.2021 03:40


Mathematics, 09.03.2021 03:40

Mathematics, 09.03.2021 03:40



Mathematics, 09.03.2021 03:40

Mathematics, 09.03.2021 03:40

History, 09.03.2021 03:40





Biology, 09.03.2021 03:40


English, 09.03.2021 03:40

Business, 09.03.2021 03:40

English, 09.03.2021 03:40

Biology, 09.03.2021 03:40

English, 09.03.2021 03:40

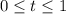 , we have
, we have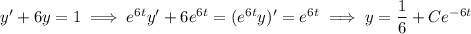
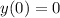 , we have
, we have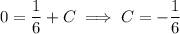
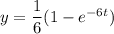
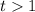 (I think you mistakenly wrote
(I think you mistakenly wrote 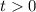 , which overlaps with the first definition of
, which overlaps with the first definition of 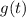 ), we have
), we have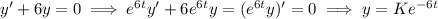
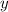 at
at 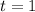 , which means we need to pick
, which means we need to pick  such that
such that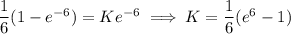
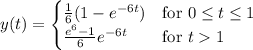
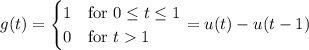
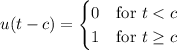
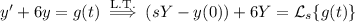
 is the Laplace transform of
is the Laplace transform of 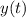 .
.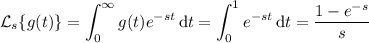

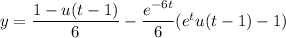
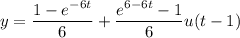
 , so that
, so that 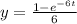 ; for
; for 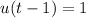 , and
, and 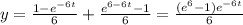 .
.

