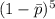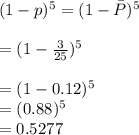Mathematics, 11.03.2020 05:30 nathanstern21
A diagnostic test for a certain disease is applied to n individuals known to not have the disease. Let X = the number among the n test results that are positive (indicating presence of the disease, so X is the number of false positives) and p = the probability that a disease-free individual's test result is positive (i. e., p is the true proportion of test results from disease-free individuals that are positive). Assume that only X is available rather than the actual sequence of test results.
(a) Derive the maximum likelihood estimator of p.
If n = 25 and x = 3, what is the estimate?
(b) Is the estimator of part (a) unbiased?
(c) If n = 25 and x = 3, what is the mle of the probability (1 - p)5 that none of the next five tests done on disease-free individuals are positive? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)

Answers: 1
Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 22:30
Atotal of 766 tickets were sold for the school play. they were either adult tickets or student tickets. there were 66 more student tickets sold than adult tickets. how many adult tickets were sold?
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:00
Atriangle in the coordinates of (2,3), (-4,5) and (-2,4) it is translated 3 units down. what are it’s new coordinates
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:20
Find the common ratio of the sequence. -4, 8, -16, 32, a: -12b: -2c: 12d: -1/-2
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:50
What is the probably of getting heads when poing a coin and getting a number greater than or equal to 5 when rolling a single diea) 1/6b) 1/3c) 1/4d) 1/12
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
A diagnostic test for a certain disease is applied to n individuals known to not have the disease. L...
Questions

Mathematics, 08.07.2019 08:00

Mathematics, 08.07.2019 08:00


English, 08.07.2019 08:00

Mathematics, 08.07.2019 08:00



Health, 08.07.2019 08:00


Mathematics, 08.07.2019 08:00

History, 08.07.2019 08:00

Mathematics, 08.07.2019 08:00


Social Studies, 08.07.2019 08:00

History, 08.07.2019 08:00

Biology, 08.07.2019 08:00

French, 08.07.2019 08:00


Mathematics, 08.07.2019 08:00

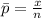
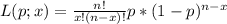
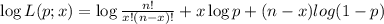
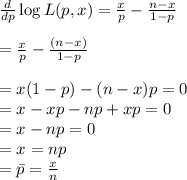
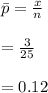
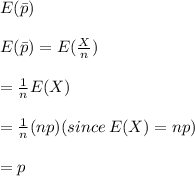
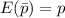 , the maximum likelihood estimate from part (a) is an unbiased estimator.
, the maximum likelihood estimate from part (a) is an unbiased estimator.
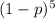 .
.
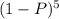 , the MLE of p can be used.
, the MLE of p can be used.