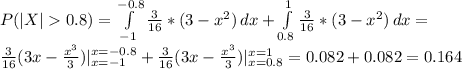Mathematics, 30.03.2020 21:35 ashleymunoz928
3.30 Measurements of scientific systems are always subject to variation, some more than others. There are many structures for measurement error, and statisticians spend a great deal of time modeling these errors. Suppose the measurement error X of a certain physical quantity is decided by the density function f(x) = k(3 − x2), −1 ≤ x ≤ 1, 0, elsewhere. (a) Determine k that renders f(x) a valid density function. (b) Find the probability that a random error in measurement is less than 1/2. (c) For this particular measurement, it is undesirable if the magnitude of the error (i. e., |x|) exceeds 0.8. What is the probability that this occurs?

Answers: 3
Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:00
Select all the correct answers. what is 221,000,000,000,000,000,000 expressed in scientific notation?
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 22:00
What value is a discontinuity of x squared plus 8 x plus 4, all over x squared minus x minus 6?
Answers: 2


Mathematics, 22.06.2019 02:30
Fred and gene are hang gliding. fred is 700 feet above the ground and descending at 15 ft/s. gene is decending as shown in the table. interpret the rates of change and initial values of the linear functions in terms of the situations they model. show all work. freds equation is f(x)=-15x+700. ( genes is the table attached)
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
3.30 Measurements of scientific systems are always subject to variation, some more than others. Ther...
Questions

History, 11.09.2019 17:20


Mathematics, 11.09.2019 17:20






Biology, 11.09.2019 17:20



Mathematics, 11.09.2019 17:20



History, 11.09.2019 17:20


Mathematics, 11.09.2019 17:20


English, 11.09.2019 17:20

![1 = k \int\limits^1_{-1} {(3-x^2)} \, dx = k * (3x-\frac{x^3}{3})|_{x=-1}^{x = 1} = k*[(3-1/3) - (-3 + 1/3)] = 16k/3](/tpl/images/0571/3484/7e564.png)
![P(X < 1/2) = \int\limits^{0.5}_{-1} {\frac{3}{16}(3-x^2)} \, dx = \frac{3}{16} [(3x-\frac{x^3}{3}) |_{x=-1}^{x=0.5}] =\frac{3}{16} *(1.458333 - (-3+1/3)) = 0.7734](/tpl/images/0571/3484/211f5.png)