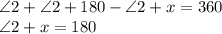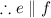Mathematics, 22.04.2020 18:59 only1cache
Given: g ∥ h and ∠2 ≅ ∠3
Prove: e ∥ f
Horizontal and parallel lines e and f are intersected by diagonal and parallel lines g and h. At the intersection of lines g and e, the bottom right angle is angle 2. At the intersection of lines h and e, the bottom right angle is angle 1. At the intersection of lines f and h, the top left angle is angle 3.
Statements Reasons
1. g || h 1. given
2. ∠1 ≅ ∠2 2. corresponding angles theorm
3. ∠2 ≅ ∠3 3. given
4. ∠1 ≅ ∠3 4. transitive property
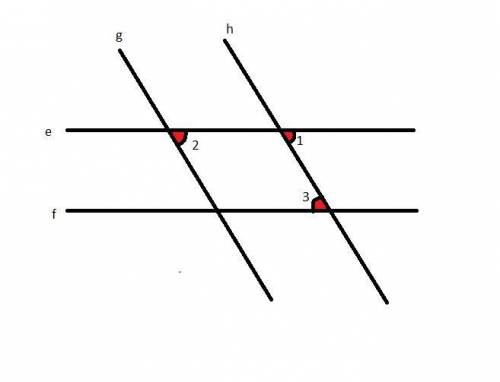
5. e || f 5. ?
What is the missing reason in the proof?
vertical angles theorem
alternate exterior angles theorem
converse corresponding angles theorem
converse alternate interior angles theorem

Answers: 2
Another question on Mathematics


Mathematics, 21.06.2019 19:30
If (17, 4) is an ordered pair of the inverse of f(x), which of the following is an ordered pair of the function f(x)? a. (17,4) b. (4.17) c. (4,0) d. 0,17)
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 00:00
Abook store is having a 30 perscent off sale. diary of the wimpy kid books are now 6.30 dollars each what was the original price of the books
Answers: 1

You know the right answer?
Given: g ∥ h and ∠2 ≅ ∠3
Prove: e ∥ f
Horizontal and parallel lines e and f...
Prove: e ∥ f
Horizontal and parallel lines e and f...
Questions

History, 28.07.2019 03:20



Biology, 28.07.2019 03:20










Social Studies, 28.07.2019 03:30




Biology, 28.07.2019 03:30

Social Studies, 28.07.2019 03:30

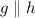 and
and  .
.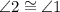 , by corresponding angles (same side of the transversal, one interior, the other exterior to parallels).
, by corresponding angles (same side of the transversal, one interior, the other exterior to parallels).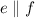 , we must demonstrate a congruence between angle 2 and an angle on the intersection between line g and line f.
, we must demonstrate a congruence between angle 2 and an angle on the intersection between line g and line f.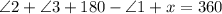
 is the angle at the intersection line g and line f.
is the angle at the intersection line g and line f.