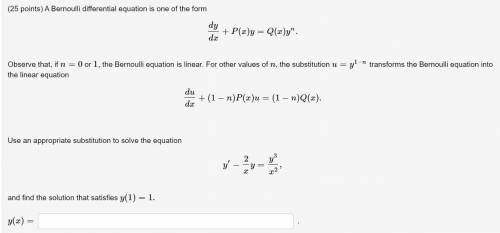
A Bernoulli differential equation is one of the form
dy/dx+P(x)y=Q(x)y^n.
Observe that...

Mathematics, 26.10.2021 18:10 realpcy7515
A Bernoulli differential equation is one of the form
dy/dx+P(x)y=Q(x)y^n.
Observe that, if n=0 or 1, the Bernoulli equation is linear. For other values of n, the substitution u=y^(1−n) transforms the Bernoulli equation into the linear equation
du/dx+(1−n)P(x)u=(1−n)Q(x).
Use an appropriate substitution to solve the equation
y′−(2/x)y=y^3/x^2,
and find the solution that satisfies y(1)=1.
y(x)=

Answers: 2
Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 12:40
Given the graph below state whether or not the relation is a function, and give the domain and range.
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 15:30
Using the quadratic formula find the zeros of the given polynomial -5x^2+3x-11
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:00
Ernest is purchasing a $175,000 home with a 30-year mortgage. he will make a $15,000 down payment. use the table below to find his monthly pmi payment.
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 17:30
Me with this one question, and i'll upvote the brainliest answer
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Questions

History, 20.05.2021 02:10




Mathematics, 20.05.2021 02:10

Mathematics, 20.05.2021 02:10

Mathematics, 20.05.2021 02:10




Chemistry, 20.05.2021 02:10

History, 20.05.2021 02:10

Mathematics, 20.05.2021 02:10


Mathematics, 20.05.2021 02:10

Mathematics, 20.05.2021 02:10

Mathematics, 20.05.2021 02:10

Mathematics, 20.05.2021 02:10





