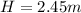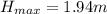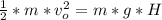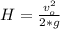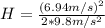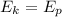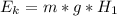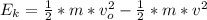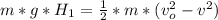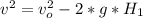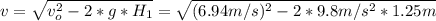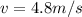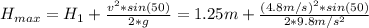Physics, 15.11.2019 20:31 leslyrivera11
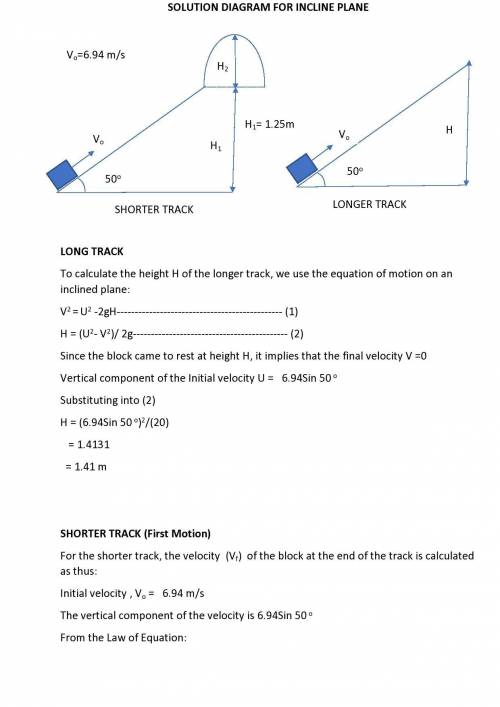
The drawing shows two frictionless inclines that begin at ground level (h = 0 m) and slope upward at the same angle θ. one track is longer than the other, however. identical blocks are projected up each track with the same initial speed v0. on the longer track the block slides upward until it reaches a maximum height h above the ground. on the shorter track the block slides upward, flies off the end of the track at a height h1 above the ground, and then follows the familiar parabolic trajectory of projectile motion. at the highest point of this trajectory, the block is a height h2 above the end of the track. the initial total mechanical energy of each block is the same and is all kinetic energy. the initial speed of each block is v0 = 6.94 m/s, and each incline slopes upward at an angle of θ = 50.0°. the block on the shorter track leaves the track at a height of h1 = 1.25 m above the ground. find (a) the height h for the block on the longer track and (b) the total height h1 + h2 for the block on the shorter track.

Answers: 2
Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 18:10
Awheelhas a radius of 4.8 m. howfar (path length) does a point on the circumference travel if thewheel is rotated through angles of 30°, 30 rad, and 30 rev,respectively?
Answers: 3

Physics, 21.06.2019 22:50
An electron and a proton have the same kinetic energy upon entering a region of constant magnetic field and their velocity vectors are perpendicular to the magnetic field. suppose the magnetic field is strong enough to allow the particles to circle in the field. note: you'll need to look up the masses for an electron and proton. 1) what is the ratio of the radii of their circular paths rp/re?
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 14:00
Why is rain likely when warm, moisture-laden air meets cold air? a) the lighter warm air will rise and cool down, causing condensation and rain. b) the cold air moves faster and pushes the warm air away, causing condensation and rain. c) the moisture in the warm air condenses on contact with the cold air, causing rain to fall. d) the cold air mixes with the warm air, reducing its temperature causing moisture to condense.
Answers: 1

You know the right answer?
The drawing shows two frictionless inclines that begin at ground level (h = 0 m) and slope upward at...
Questions




History, 24.07.2019 08:30


Mathematics, 24.07.2019 08:30

Mathematics, 24.07.2019 08:30


Mathematics, 24.07.2019 08:30


History, 24.07.2019 08:30

Computers and Technology, 24.07.2019 08:30

History, 24.07.2019 08:30





Chemistry, 24.07.2019 08:30