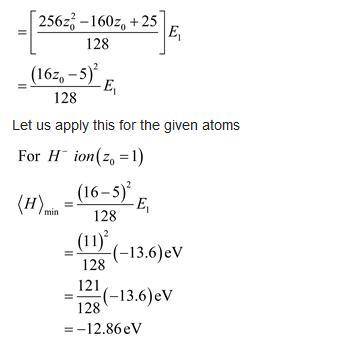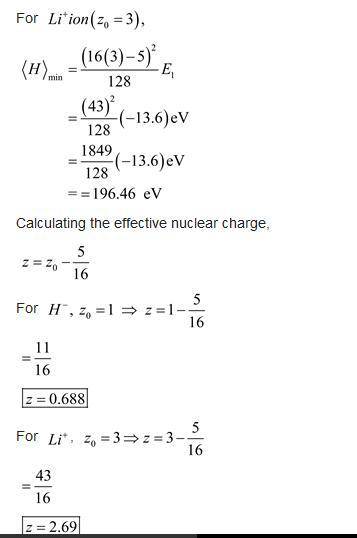Physics, 20.03.2020 11:00 fatherbamboo
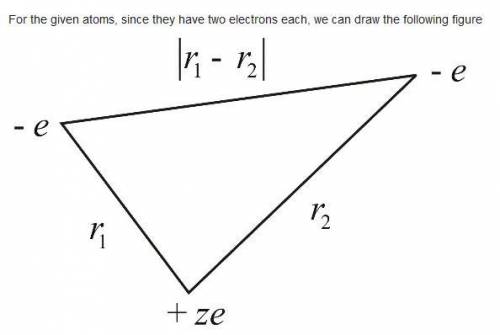
Apply the techniques of this Section to the H − and Li + ions (each has two electrons, like helium, but nuclear charges and , respectively). Find the effective (partially shielded) nuclear charge, and determine the best upper bound on , for each case. Comment: In the case of H − you should find that eV, which would appear to indicate that there is no bound state at all, since it would be energetically favorable for one electron to fly off, leaving behind a neutral hydrogen atom. This is not entirely surprising, since the electrons are less strongly attracted to the nucleus than they are in helium, and the electron repulsion tends to break the atom apart. However, it turns out to be incorrect. With a more sophi

Answers: 3
Another question on Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 00:30
Asap time is ! best answer gets compose at least one well-developed paragraph on the following: define the term concurrent powers, and give an example of a concurrent power of government.
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 05:30
Blank liquids and gases exert a buoyant force on objects placed in them
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 12:00
Explain why electric current cannot exist if a current doesn't have a voltage source.
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 17:00
Since the energy was not raising the temperature of the water during these segments, what was the energy used to do instead? your answer must include an explanation of what is happening to the molecules.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Apply the techniques of this Section to the H − and Li + ions (each has two electrons, like helium,...
Questions

Computers and Technology, 25.02.2020 21:57





History, 25.02.2020 21:57


Mathematics, 25.02.2020 21:57

Mathematics, 25.02.2020 21:57


Chemistry, 25.02.2020 21:57


Health, 25.02.2020 21:57







Computers and Technology, 25.02.2020 21:58