Physics, 05.05.2020 00:44 nadia00738
To understand and be able to use the rules for determining allowable orbital angular momentum states.
Several numbers are necessary to describe the states available to an electron in the hydrogen atom. The principal quantum number n determines the energy of the electron. The orbital quantum number l determines the total angular momentum of the electron, and the magnetic quantum number ml determines the component of the angular momentum parallel to a specific axis, usually the z axis.
For a given principal quantum number n, the orbital quantum number can take integer values ranging from zero to n−1. For a given orbital quantum number l, the magnetic quantum number can take integer values from −l to l. A fourth number, the spin ms, is important for interactions with magnetic fields and counting states. The spin can be either +1/2 or −1/2, independent of the values of the other quantum numbers.
The energy of an electron in hydrogen is related to the principal quantum number by En=(−13.60eV)/n^2. The orbital angular momentum is related to the orbital quantum number by L=ℏ√l(l+1), and the orbital angular momentum in the z direction is related to the magnetic quantum number by Lz=mlℏ.
Required:
a. How many different values of I are possible for an electron with principal quantum number n= 5?
b. How many values of mi are possible for an electron with orbital quantum number I= 3?
c. The quantum state of a particle can be specified by giving a complete set of quantum numbers (n, l, mi, ms). How many different quantum states are possible if the principal quantum number is n= 3?
d. Is the state n =3, I =3, m= —2, ms =1/2 an allowable state? If not, why not?
e. What is the maximum angular momentum Lmax that an electron with principal quantum number n= 3 can have?

Answers: 2
Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 18:00
How are momentum and impulse related? impulse is a whim to do something, while momentum keeps it going impulse is another name fore instantaneous momentum the impulse acting on and object is equal to the change of momentum it causes. the impulse that acts on and object is the momentum that results.
Answers: 2

Physics, 21.06.2019 23:00
How many dots must be added to the symbol to properly represent a standard nitrogen ion? a) 1 b) 3 c) 5 d) 8
Answers: 1


Physics, 22.06.2019 12:00
Ihave a density of 1.61g/cm^3 and a mass of 28g. find the missing value
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
To understand and be able to use the rules for determining allowable orbital angular momentum states...
Questions

History, 06.11.2020 03:10

History, 06.11.2020 03:20



Mathematics, 06.11.2020 03:20

Physics, 06.11.2020 03:20


Mathematics, 06.11.2020 03:20


English, 06.11.2020 03:20





Health, 06.11.2020 03:20

Mathematics, 06.11.2020 03:20

Chemistry, 06.11.2020 03:20

Mathematics, 06.11.2020 03:20

Mathematics, 06.11.2020 03:20

Mathematics, 06.11.2020 03:20

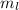 = 7
= 7