Physics, 21.03.2021 01:00 reagancunningham2004
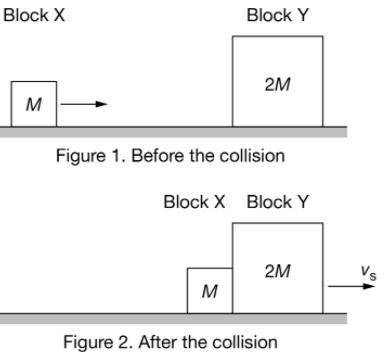
Block X of mass M slides across a horizontal surface where friction is negligible. Block X collides with block Y of mass 2M that is initially at rest, as shown in Figure 1. After the collision, both blocks slide together with a speed vs, as shown in Figure 2. If the two-block system moves at 1.5 m/s after the collision, what was the initial speed of Block X immediately before the collision?

Answers: 2
Another question on Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 13:30
Global warming will produce rising sea levels partly due to melting ice caps but also due to the expansion of water as average ocean temperatures rise. to get some idea of the size of this effect, calculate the change in length of a column of water 1.00 km high for a temperature increase of 1.00ºc. note that this calculation is only approximate because ocean warming is not uniform with depth. (answer in ×10^{-3} −3 m)
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 16:00
The electric potential v is constant everywhere within a certain region of space. which statement below is true? the choices are: the electric field is also constant (but not zero) within the region. a charged particle placed within the region will experience an electric force. the electric field is zero everywhere within the region. the electric field varies from place to place within the region.
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 16:30
3. a lunar exploration vehicle was created by a research team. it weighs 3,000 kg on the earth. it needs an acceleration of 10 m/s2 on the moon. in order to have the same acceleration, what will be the net force acting on the vehicle on the earth?
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 20:20
Consider a file currently consisting of 200 blocks. assume that the file control block (and the index block in the case of indexed allocation) is already in memory. calculate how many disk i/o operations are required for contiguous, linked, and indexed (single-level) allocation strategies, for each of the conditions listed below. in the contiguous-allocation case, assume that there is not room to grow at the beginning but there is room to grow at the end. also assume that the block information to be added is stored in memory.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Block X of mass M slides across a horizontal surface where friction is negligible. Block X collides...
Questions



Biology, 05.03.2021 09:10

History, 05.03.2021 09:10

Mathematics, 05.03.2021 09:10

Mathematics, 05.03.2021 09:10

Mathematics, 05.03.2021 09:10



Social Studies, 05.03.2021 09:10


Mathematics, 05.03.2021 09:10

Mathematics, 05.03.2021 09:10


Computers and Technology, 05.03.2021 09:10

Computers and Technology, 05.03.2021 09:10

Mathematics, 05.03.2021 09:10

Chemistry, 05.03.2021 09:10

Mathematics, 05.03.2021 09:10