
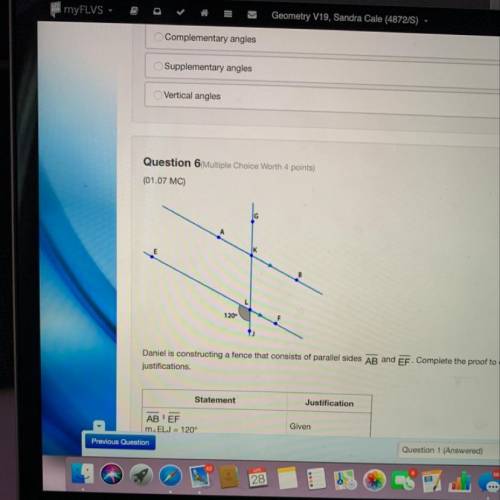
Daniel is constructing a fence that consists of parallel sides AB and EF. Complete the proof to explain how he can show that m. GKB-120 by filling in the missing
justifications
Statement
Justification
AB EF
m. ELJ 120"
Given
m. ELJ + m. ELK - 180°
Linear Pair Postulate
m BKL m GKB-180
Linear Pair Postulate
m. ELJ + m. ELKm
BKL
m. GKB Transitive Property
ELK - BKL
m. ELKm .BKL
m. ELJ + m. ELK
m. ELK+m GKB Substitution Property
Subtraction Property
m. ELJ - m GKB
m. GKB-m. ELJ
Symmetric Property
m. GKB120
Substitution
1. Alternate Interior Anglos Theorem; 2. Definition of Congruence
1. Alternate Exterior Anglos Theorem: 2. Substitution Property
1. Definition of Congruence; 2. Alternate Interior Anglos Theorem
1. Substitution Property, 2. Alternate Exterior Anglos Theorem

Answers: 1
Another question on Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 20:00
If a cell's main function is to produce proteins to be excreted, which organelles would you expect to be larger
Answers: 2

Biology, 21.06.2019 20:30
Match the descriptions / definitions with the term they best describe 1. three dimensional relationship of the different polypeptide chains in a multisubunit protein or protein complex 2. common folding pattern in proteins in which a linear sequence of amino acids folds into a right-handed coil stabilized by internal hydrogen-bonding between polypeptide backbone atoms. 3. the amino acid sequence of a protein 4. a region on the surface of a protein that can interact with another molecule through noncovalent bonding. 5. three-dimensional arrangement of alpha-helices and beta-sheets within a single polypeptide, typically stabilized by a variety of noncovalent bonds, including ionic and hydrogen bonds, and nonpolar interactions / hydrophobic force. 6. the chain of repeating carbon and nitrogen atoms, linked by peptide bonds, in a protein. 7. common structural motif in proteins in which different sections of the polypeptide chain run alongside each other and are joined together by hydrogen bonding between atoms of the polypeptide backbone. 8. portion of a polypeptide chain that has a discrete tertiary structure of its own and can often fold independently of the rest of the chain 9. regular local folding patterns in a protein, including alpha-helix and beta-sheet a. primary structure b. beta-sheet c. protein d. coiled-coil e. polypeptide backbone f. secondary structure g. side chain h. tertiary structure i. binding site j. alpha-helix k. quaternary structure l. protein domain
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 08:40
What best explains whether bromine (br) or neon (ne) is more likely to form a covalent bond? bromine forms covalent bonds because it has seven valence electrons, but neon has eight valence electrons and already fulfills the octet rule. bromine forms covalent bonds because it has many electron shells, but neon has only two electron shells and is tightly bound to its electrons. neon forms covalent bonds because it can share its valence electrons, but bromine has seven valence electrons and can gain only one more electron. neon forms covalent bonds because it has only two electron shells, but bromine has many electron shells and will lose electrons in order to fulfill the octet rule.
Answers: 3

Biology, 22.06.2019 10:30
Which is a function of vascular tissue? a. to perform photosynthesis b. to transport water and nutrients c. to absorb minerals and sugar d. to interact with soil fungi
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Daniel is constructing a fence that consists of parallel sides AB and EF. Complete the proof to expl...
Questions









English, 10.12.2019 19:31













