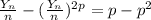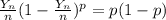Let the random variable yn have a distribution that is b(n, p).
(a) prove that yn/n con...

Mathematics, 25.12.2019 07:31 Amyra2003
Let the random variable yn have a distribution that is b(n, p).
(a) prove that yn/n converges in probability to p. this result is one form of the weak law of large numbers.
(b) prove that 1 − yn/n converges in probability to 1 − p.
(c) prove that (yn/n)(1 − yn/n) converges in probability to p(1 − p).

Answers: 2
Another question on Mathematics


Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:00
Data are collected to see how many ice-cream cones are sold at a ballpark in a week. day 1 is sunday and day 7 is the following saturday. use the data from the table to create a scatter plot.
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 19:10
The linear combination method is applied to a system of equations as shown. 4(.25x + .5y = 3.75) → x + 2y = 15 (4x – 8y = 12) → x – 2y = 3 2x = 18 what is the solution of the system of equations? (1,2) (3,9) (5,5) (9,3)
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 01:30
Given a binomial distribution variable with n=20 and p=0.60 find the following possibilities using the binomial table a) p(x < 13) b) p x > 15) c) p(x = 17) d) p(11 < x < 14) e) p(11 < x < 14)
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Questions


Mathematics, 20.02.2020 23:53








History, 20.02.2020 23:53


Mathematics, 20.02.2020 23:53








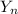 have a distribution thst id b(n, p)
have a distribution thst id b(n, p)![Pr[[\frac{Y_n}{n}-E[\frac{Y_n}{n}]\geq E]\leq\frac{1}{E^2}var[\frac{Y_n}{n}]\\\\=Pr[(\frac{Y_n}{n}-P)\geq E]\leq \frac{1}{n^2E^2}np(1-p)=0](/tpl/images/0432/7085/7815a.png)
![\frac{Y_n^P}{n}=PB)As mentioned in a), use chebyshevs inequality.[tex]Pr(\frac{Y_n}{n}-E(\frac{Y_n}{n})\geq E)\leq \frac{1}{E^2}var(\frac{Y_n}{n})](/tpl/images/0432/7085/4934a.png)
![Pr[(1-\frac{Y_n}{n}-(1-p))\geq E]\leq \frac{1}{n^2E^2}np(1-p)=0](/tpl/images/0432/7085/34352.png)
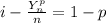
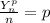 obtained the following
obtained the following ![[\frac{Y_n}{n}]^2^p=p^2](/tpl/images/0432/7085/34cad.png)