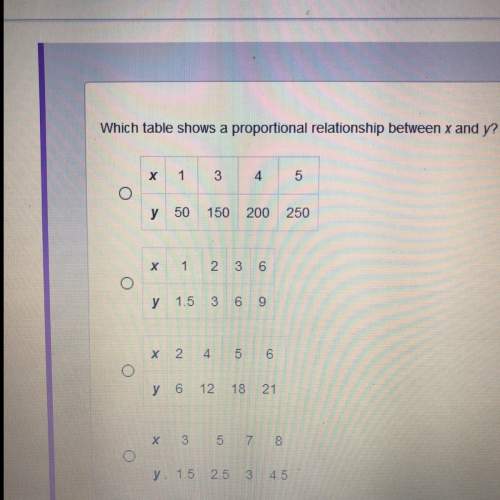
Mathematics, 09.11.2020 17:00 khandjia
Answer the following questions about confidence intervals.
(a) What happens to a confidence interval as sample sizeincreases, assuming everything else stays the same?
The width of the interval decreases, since the standard error decreases. The center of the interval decreases, since the standard error increases. The center of the intervalincreases, since the standard error decreases. The width of the interval increases, since the standard error increases.
(b) If we want to use a larger confidence level when creating a confidence interval for a population mean, which of the following happens to our confidence interval?
The interval gets wider, since the standard error decreases. The interval gets narrower, since the t-value required to capture a larger proportion of the sampling distribution of the sample mean gets smaller. The interval gets narrower, since the standard error decreases. The interval gets wider, since the t-value required to capture a larger proportion of the sampling distribution of the sample mean gets larger.
(c) What does the margin of error in a confidence interval for a population mean describe?
It describes the difference between the sample mean and the population mean due to calculation errors by the researchers. It describes the difference between the sample mean and the population mean. Due to the random sampling method, different sample means will be different. It describes the difference between the sample mean and the population mean, due to taking non-random samples involving voluntary response or convenience sampling. It describes how often researchers make a mistake due to response bias or non-response bias.
(d) Why do we use a z-score from a normal distribution in constructing large-sample confidence intervals for a proportion?
For large random samples the data distribution is approximately normal. For any n we use the t-distribution to get a confidenceinterval, and for large n the t-distribution looks like the standard normal distribution. For large random samples the sampling distribution of the sample proportion is approximately normal. The population distribution is normal for large samples.
(e) True or false: The confidence interval for a mean with a random sample of size n = 2000 is invalid if the population distribution is bimodal.
TrueFalse

Answers: 3
Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:40
Dexter read 11 science fiction books and 5 history books. lena read 9 science fiction books and 4 history books. compare the students’ ratios of science fiction books to history books. 1. determine the ratios’ form: science fiction books to history books 2. write the ratios as fractions: dexter: 115; lena: 94 3. rewrite with a common denominator. 4. compare. 5. answer the question. determine which shows the correct comparison of the ratios for this problem.
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:10
Which value of m will create a system of parallel lines with no solution? y = mx - 6 8x - 4y = 12
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 21:30
Atrain leaves little? rock, arkansas, and travels north at 90 kilometers per hour. another train leaves at the same time and travels south at 80 kilometers per hour. how long will it take before they are 680 kilometers? apart?
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 22:30
An ant travels at a constant rate of 30cm every 2 minutes.at what speed does the ant travel per minute
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Answer the following questions about confidence intervals.
(a) What happens to a confidence interva...
Questions


Mathematics, 07.11.2020 01:00

Mathematics, 07.11.2020 01:00

History, 07.11.2020 01:00



Mathematics, 07.11.2020 01:00


Mathematics, 07.11.2020 01:00

Mathematics, 07.11.2020 01:00

History, 07.11.2020 01:00


Social Studies, 07.11.2020 01:00

Mathematics, 07.11.2020 01:00




Mathematics, 07.11.2020 01:00

Mathematics, 07.11.2020 01:00

Health, 07.11.2020 01:00