
Mathematics, 12.11.2020 09:50 cschuessler3
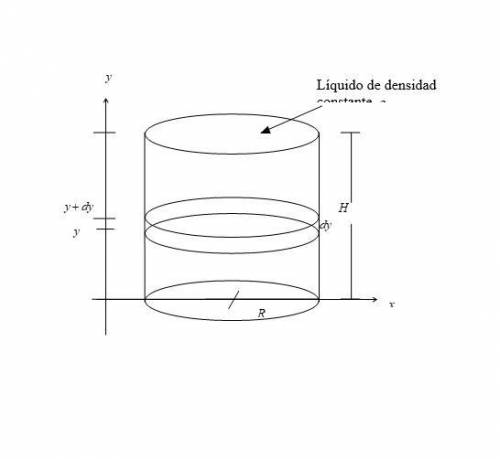
Ejercicio 2: Supongamos que se tiene un recipiente cilíndrico de radio y altura lleno de un líquido de densidad constante y que se desea vaciar el contenido llevando el líquido a la parte superior del recipiente. Calcula el trabajo que se requiere para llevar a cabo esta tarea, realizando los pasos que se te piden.
Ayuda: Para calcular el trabajo para vaciar el recipiente se puede pensar en seccionar el contenido del recipiente en un número infinito de elementos cilíndricos de radio y anchura (ver figura inferior) y calcular el trabajo que se tiene que realizar para llevar cada una de estas secciones a la parte superior del recipiente.
a) Calcula el diferencial de volumen de uno de estos elementos cilíndricos de anchura .
_
b) Calcula el diferencial de masa correspondiente.
_
c) Calcula el diferencial de peso correspondiente.
_
d) Calcula el diferencial de trabajo necesario para subir hasta la parte superior del recipiente el elemento cilíndrico.
_
e) Finalmente calcula el trabajo total para vaciar el recipiente.
_

Answers: 3
Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:00
What power can you write to represent the volume of the cube shown? write the power as an expression with a base and an exponent and then find the volume of the cube
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:00
Solve this equation using substitution. {4x + y = −2} {4x + 6y = 44}
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 21:30
About 9% of th population is hopelessly romantic. if 2 people are randomly selected from the population, what is the probability that at least 1 person is hopelessly romantic?
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 00:00
Aspacecraft can attain a stable orbit 300 kilometers above earth if it reaches a velocity of 7.7 kilometers per second. the formula for a rocket's maximum velocity v in kilometers per second is vequalsminus0.0098tplusc ln upper r, where t is the firing time in seconds, c is the velocity of the exhaust in kilometers per second, and r is the ratio of the mass of the rocket filled with fuel to the mass of the rocket without fuel. find the velocity of a spacecraft whose booster rocket has a mass ratio of 20, an exhaust velocity of 2.1 km/s, and a firing time of 15 s. can the spacecraft achieve a stable orbit 300 km above earth?
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Ejercicio 2: Supongamos que se tiene un recipiente cilíndrico de radio y altura lleno de un líquido...
Questions













Mathematics, 30.10.2020 16:20


Computers and Technology, 30.10.2020 16:20

Computers and Technology, 30.10.2020 16:20


Computers and Technology, 30.10.2020 16:20





